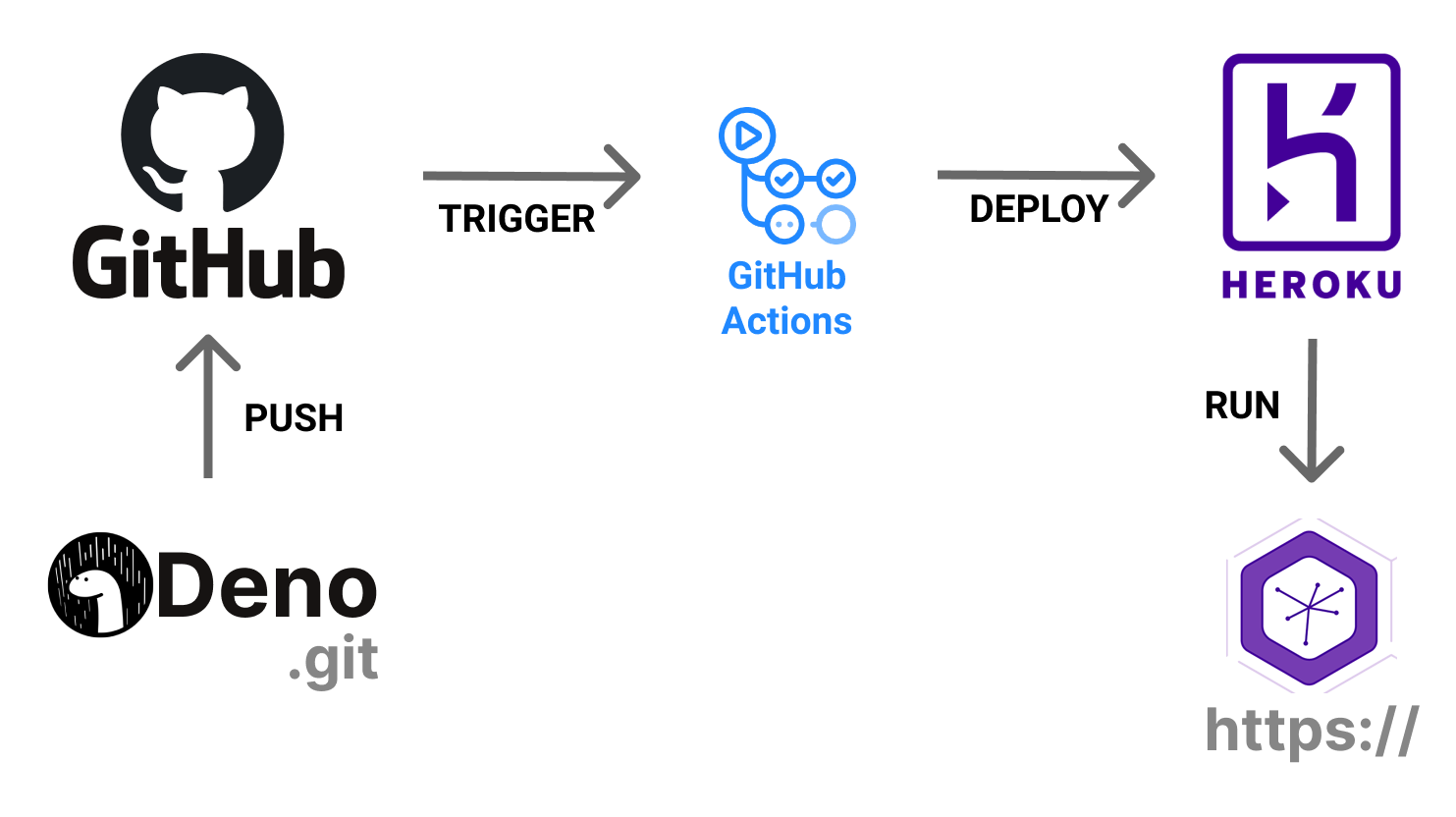
Let’s Deploy a Deno App to Heroku 🦕
We have already developed a REST API using Deno on Linux, protected it with the JWT authentication, and connected it to the MongoDb Atlas. To complete this story, we need to configure our deployment process and deploy the app to the cloud. So this is what this video is about, let’s get started.
Task description
- Deploy a deno app
- Deploy on push to the main branch
- Run unit tests
- Run lint
GitHub
- Create a repository (if you hadn’t created it so far)
- Upload the source code to the repository
Heroku
Create an app
- Create a new app
- Choose the deployment method as GitHub
- Connect the GitHub repo to the app
- Turn on automatic deploys
- Settings > Add a build pack https://github.com/chibat/heroku-buildpack-deno.git
Procfile
Next, we need to create a Procfile. Procfile is a mechanism for declaring what commands are run by your application’s dynos on the Heroku platform.
- Add a Procfile to the project with the following content:
web: deno run --allow-net --allow-env --allow-read mod.ts --port=${PORT}
- Pay attention to permission flags.
-Amay not be the best choice. Don’t grant more permissions than the app actually needs
GitHub (Continue)
- Setup the GitHub Actions (pipeline)
- Setup a new workflow
- Use the following yaml template:
name: Deno
on:
push:
branches: [main]
pull_request:
branches: [main]
jobs:
test:
runs-on: $ # runs a test on Ubuntu, Windows and macOS
strategy:
matrix:
deno: ["v1.x", "nightly"]
os: [macOS-latest, windows-latest, ubuntu-latest]
steps:
- name: Setup repo
uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Setup Deno
uses: denolib/setup-deno@v2
with:
deno-version: $ # tests across multiple Deno versions
- name: Cache Dependencies
run: deno cache deps.ts
- name: Lint
run: deno lint --unstable
- name: Unit tests
run: deno test --allow-env --allow-read
- Run
- Review the output
Heroku (continue)
- Test the app
The Heroku platform passes a port for the application via the arguments. If the source code doesn’t have this logic, then add it to the mod.ts:
const DEFAULT_PORT = 8000;
const argPort = parse(Deno.args).port;
await app.listen({ port: argPort ?? DEFAULT_PORT });
The parse function can be imported from the https://deno.land/std/flags/mod.ts.
- Push the source code
- View the running logs
- Add the Config Vars at the Settings tab (if necessary)
Conclusion
Now we have the configured deployment process, with lint and unit tests. The application deploys automatically, runs in the cloud, and connects to the MongoDb Atlas. Let me know if you have any questions in the comments below, I hope you enjoyed this video, and I’ll see you next time.
Resources:
